Cytosol Definition
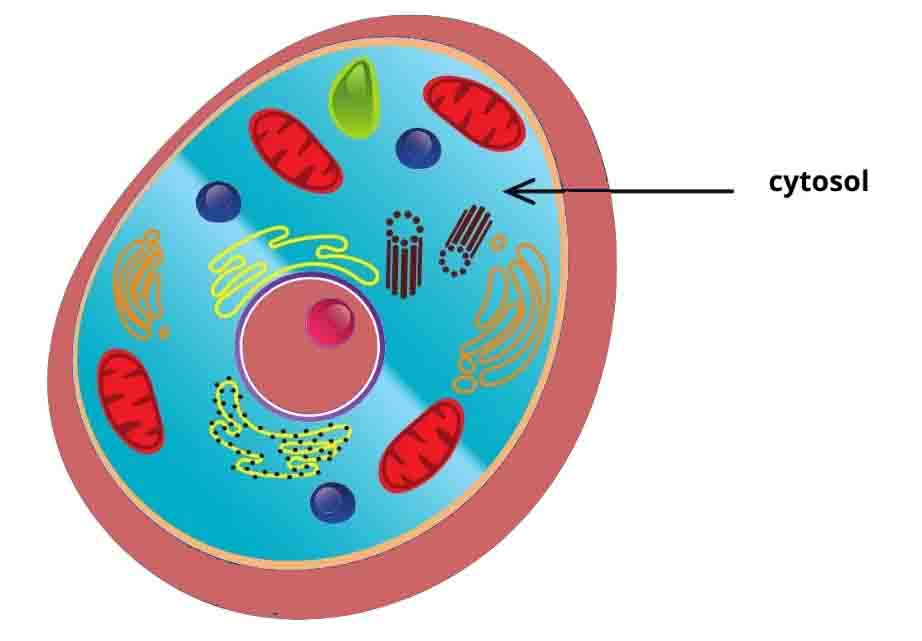
The cytosol is the liquid found inside cells. Water-based solution in which organelles, proteins, and other cell structures float.
In every cell, the cytosol is a complex solution, whose properties enable life to function. Proteins, amino acids, mRNA, ribosomes, sugars, ions, messenger molecules, and more are all found in the cytosol!
In recent years, scientists have discovered that cytosol can have structure and organization, despite once being thought to be a simple solution. Gradients of ions or messenger particles, for example, are used by some cells to carry important information.
From the fertilized egg cell, some species direct embryonic growth by organizing their cytoplasm. There is a difference in the distribution of messenger molecules throughout the egg cell’s cytoplasm in these species.
Following fertilization, the egg cell divides into different daughter cells that receive different messenger molecules – and subsequently develop into different tissues.
Previously, the cytoplasm was thought to be nothing more than salt water. This principle shows how complex and important it is!
In the cytosol, membrane-bound organelles float, but their interiors aren’t considered to be part of it. Within cells, chloroplasts, mitochondria, nuclei, and other closed, self-contained membranes have their own internal fluids and chemistry.
Function of Cytosol
The cytosol is the medium for intracellular processes. For cytosolic activities to take place, it must contain the right proteins, ions, and other ingredients.
The cytosol is involved in the following activities:
1. Activities of enzymes. To function properly, enzymes require certain salt concentrations, pH levels, and other environmental conditions.
2. Transduction of signals. It is possible for messenger molecules to diffuse through the cytosol to change enzyme activity, organelle function, and even DNA transcription. They may be messengers from outside the cell, or they may be messengers within the cell.
Here is a diagram showing how signaling molecules can affect protein functions and even the nucleus of a cell through the cytosol.
3. The structure of the cell and its organelles. It is the volume of cytosol that gives most cells their shape and allows chemicals to move around.
4. DNA transcription and replication, glycolysis, etc., occur in the cytosol of prokaryotes which lack membrane-bound organelles.
Related Biology Terms
- Cell – A basic unit of life that makes up all organisms.
- Cytoplasm – The total contents of the cell. Organelles themselves as well as the cytosol – the fluid surrounding them – fall under this category.
- Extracellular fluid – The fluid outside of a cell. In addition to separating extracellular fluid from the cytosol, the cell membrane ensures that the cytosol is properly formulated.