Emulsify
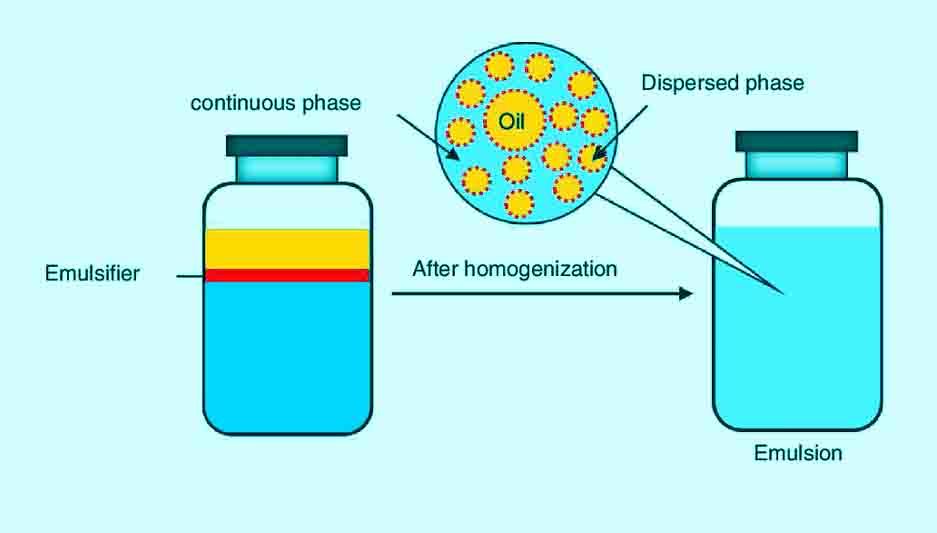
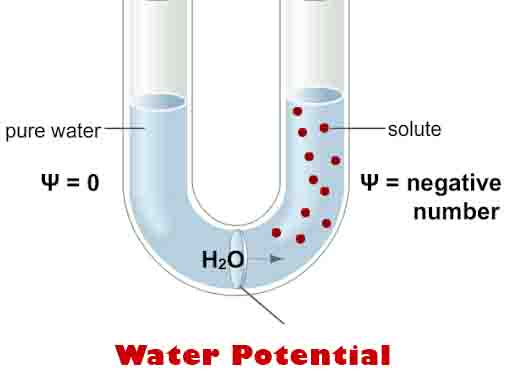
Emulsify Definition Emulsification, or to emulsify something, is defined as the mixing of two liquids that usually are unmixable together to form an emulsion. Two liquids can form different types of emulsions depending on which liquid was dispersed in which, with one liquid being the dispersed phase and the other being the external phase, which … Read more